Static Webpage Hosting on AWS: An Architectural Guide
Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
Introduction
This blog post explores a comprehensive AWS-based architecture for hosting static webpages that combines security, performance, and scalability. The solution leverages multiple AWS services to create a robust infrastructure that can host a page and maintaining basic security posture.
Architecture Overview
The static webpage hosting solution is built on a multi-layered AWS architecture that provides global content delivery, authentication, and high availability. The design follows AWS best practices for security, performance, and cost optimization.
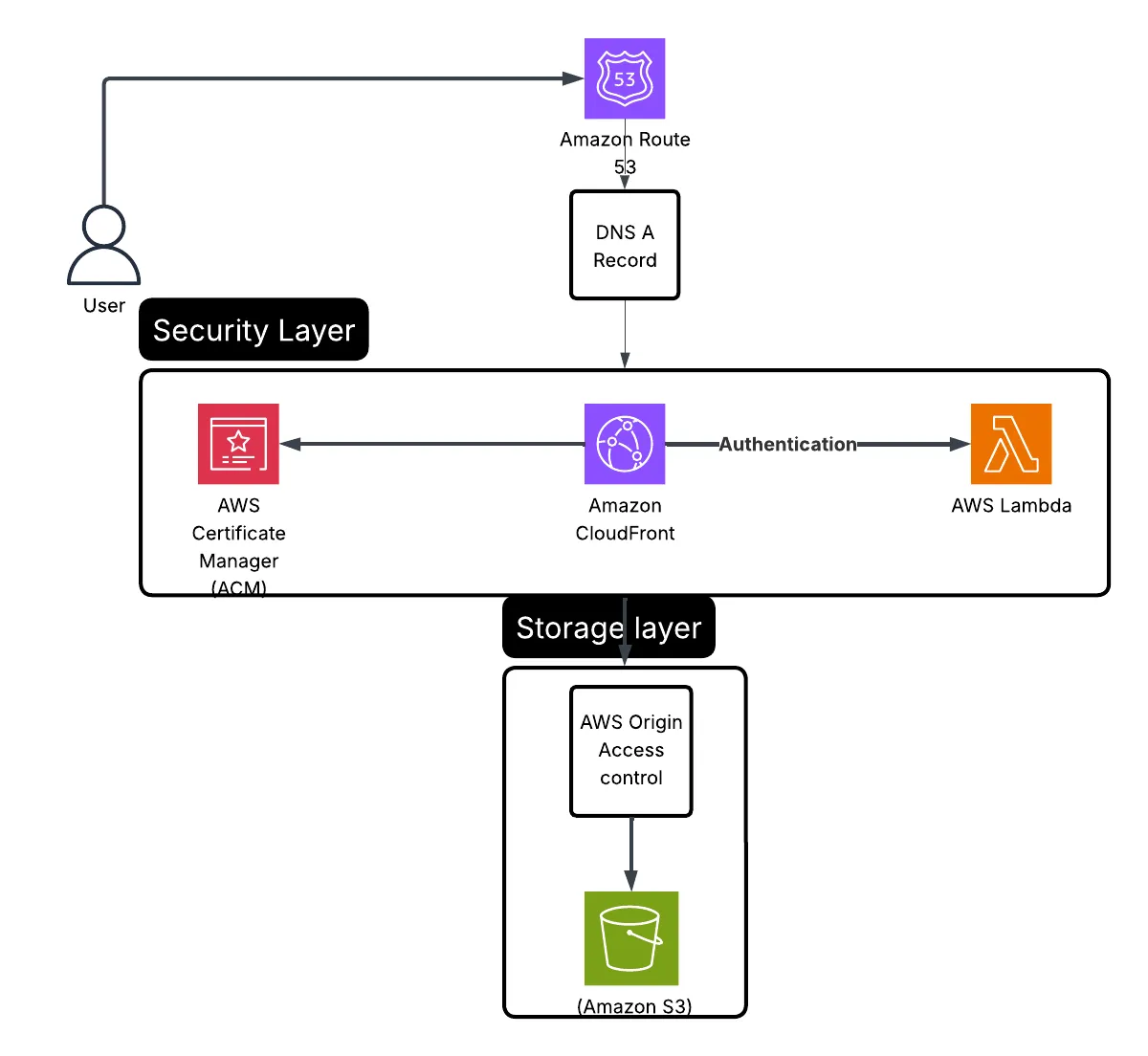
Figure 1: Static Webpage Hosting Architecture - An overview of the AWS services used in the architecture.
Core Components
Amazon S3 Storage
Purpose: Primary storage for static website content
Amazon S3 serves as the foundation storage layer for hosting static website documentation. The S3 bucket is specifically configured with a <NAME> naming pattern to store pre-built HTML documentation files. The bucket maintains a structured directory hierarchy with content organized under a /html path, which aligns with common static site generation workflows.
The bucket is secured with a restrictive policy that only allows the CloudFront service principal to access the content, ensuring that users cannot bypass the CDN and authentication layers to access files directly. This configuration provides both security and performance benefits by forcing all traffic through the optimized CloudFront distribution while maintaining the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of S3 storage.
Amazon CloudFront CDN
Purpose: Global content delivery network for fast, secure content distribution
CloudFront acts as the primary entry point for all user traffic in this architecture, serving as both a performance accelerator and security gateway. The distribution is configured with custom domain support, allowing the static website to be served from branded subdomains rather than generic CloudFront URLs. The service enforces HTTPS-only access through a viewer protocol policy that automatically redirects HTTP requests to HTTPS, ensuring all communications are encrypted. CloudFront’s global edge network caches static content at over 400 locations worldwide, dramatically reducing latency for users regardless of their geographic location. The distribution uses AWS managed caching policies optimized for static content delivery, automatically handling compression and cache headers to maximize performance while minimizing origin requests to S3.
Lambda@Edge Authentication
Purpose: Serverless authentication layer running at CloudFront edge locations
Lambda@Edge provides a lightweight but effective authentication mechanism that runs at CloudFront edge locations, processing requests before they reach the origin. In this project, the function implements Basic HTTP Authentication, requiring users to provide valid credentials before accessing the static documentation. The authentication logic is embedded in a Node.js function that intercepts viewer requests, validates authorization headers against predefined credentials, and either allows the request to proceed or returns a 401 Unauthorized response. This approach provides global authentication without the need for a centralized authentication server, reducing latency and infrastructure complexity. The function automatically scales with CloudFront traffic and only executes when needed, making it extremely cost-effective for protecting static documentation sites.
Authentication Flow:
The authentication process follows a simple but effective pattern: when a user requests the webpage, the Lambda@Edge function intercepts the request at the CloudFront edge, validates the provided authorization header against configured credentials, and either returns a 401 Unauthorized response for invalid credentials or allows the request to proceed to the origin for valid ones. This ensures that content is served from cache or origin only after successful authentication.
Route53 DNS Management
Purpose: DNS resolution and traffic routing
Route53 serves as the authoritative DNS service for the project, managing domain resolution for both www and non-www variants of the static website subdomain. The service is configured with A records that use alias functionality to point directly to the CloudFront distribution, providing efficient routing without the overhead of CNAME records.
The DNS setup supports multiple subdomain patterns, allowing different services to have their own documentation endpoints under the same hosted zone. Route53’s global anycast network ensures that DNS queries are resolved from the nearest location, minimizing latency for the initial domain resolution. The service maintains high availability with a 100% SLA and can be configured with health checks to automatically route traffic away from unhealthy endpoints if needed.
AWS Certificate Manager
Purpose: SSL/TLS certificate management for secure connections
AWS Certificate Manager handles all SSL/TLS certificate provisioning and management for the project’s custom domains. The service automatically provisions free SSL certificates that are specifically validated for the subdomain patterns used by the static website hosting infrastructure. ACM integrates seamlessly with CloudFront, automatically renewing certificates before expiration without any manual intervention. The certificates support both the primary subdomain and wildcard patterns, allowing for flexible subdomain usage across different services. This automated certificate management eliminates the operational overhead of manual certificate renewal and ensures continuous HTTPS availability for all hosted documentation sites. Creating the certificate however takes time as AWS needs to validate domain ownership.
Deployment Workflow
The typical deployment process follows these steps:
-
Content Preparation
- Build static website content
- Generate HTML, CSS, JavaScript files
- Organize files in appropriate directory structure
-
S3 Upload
- Upload files to S3 bucket
- Maintain
/htmldirectory structure - Set appropriate object metadata
-
CloudFront Invalidation
- Create invalidation for updated content
- Ensure fresh content delivery
- Monitor invalidation completion
-
DNS Propagation
- Route53 changes propagate globally
- TTL settings control propagation speed
- Health checks verify service availability
Cost Considerations
The architecture provides cost-effective hosting through:
1. S3 Storage Costs
- Pay only for storage used
- Intelligent tiering available for infrequently accessed content
- No minimum storage requirements
2. CloudFront Pricing
- Pay per GB transferred
- Free tier includes 1TB of data transfer
- Regional pricing variations
3. Lambda@Edge Costs
- Pay per request and execution time
- Minimal cost for authentication function
- No idle time charges
4. Route53 Costs
- Fixed cost per hosted zone
- Pay per DNS query
- Health check costs if implemented
Conclusion
This AWS-based static webpage hosting architecture provides a simple, secure, and scalable solution for modern web applications. By leveraging CloudFront’s global edge network, S3’s reliable storage, Lambda@Edge’s authentication capabilities, and Route53’s DNS management, organizations can deliver fast, secure web experiences to users. The architecture strikes an optimal balance between security, performance, and cost-effectiveness while maintaining operational simplicity. The use of Infrastructure as Code (Terraform) ensures reproducible deployments and consistent environments across development, staging, and production. This architecture serves as a solid foundation for organizations looking to host static websites, documentation sites, or single-page applications with enterprise-grade security and performance requirements.